10 Eye-Opening Facts on Autism’s Effect on Education

Key Points:
- The effects of autism on education vary across children, with social, communication, and behavioral challenges impacting learning.
- Autism often requires tailored teaching methods that accommodate different learning styles.
- Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy plays a key role in helping children with autism thrive in educational settings.
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) affects 1 in 31 children in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This number highlights the growing need for awareness and understanding about how autism affects a child’s daily life, including in the educational setting.
For parents, understanding how autism impacts their child’s learning environment is crucial to providing the necessary support and creating a positive educational experience. In this article, we’ll go over how autism affects education and how interventions like ABA therapy can be beneficial.
Does Autism Affect Education?
Yes, the effects of autism on education are significant and diverse. Children with autism may face challenges with communication, social interaction, and behavioral responses, which can make typical classroom environments difficult. Understanding these challenges is key to creating supportive educational settings where these children can thrive.
Autistic students often display varying levels of difficulty in areas such as language acquisition, attention, socialization, and sensory processing. These difficulties, while not always the same for each child, directly affect their ability to engage in traditional teaching methods. Schools need to adapt to these needs, either through specialized programs, personalized educational plans, or therapeutic interventions.
10 Facts About Autism and Education
Understanding how autism intersects with education is essential for parents, teachers, and caregivers working to support academic and developmental growth. Educational needs vary widely among students on the spectrum, making individualized approaches not just helpful, but necessary.
From specialized support services to tailored classroom strategies, knowing the facts about autism and education can help ensure that children receive the tools and support they need to thrive in school settings. Below are some important facts about autism and education:
1. Communication Barriers Can Hinder Learning
Children with autism often struggle with both verbal and non-verbal communication, which directly impacts their ability to participate in classroom discussions, express their needs, and interact with peers.
While some children may develop speech and language skills at a slower pace, others may be nonverbal. This communication barrier can create frustration and hinder the child’s ability to engage with teachers and peers effectively.
In educational settings, this can manifest in various ways:
- Difficulty answering questions or following verbal instructions.
- Challenges in making eye contact or engaging in back-and-forth conversation.
- Struggles with understanding figurative language, like idioms, jokes, or sarcasm.
Teachers who are aware of these challenges can provide alternative methods of communication, such as visual supports, sign language, or communication devices.
2. Social Skills are Often Delayed
Social difficulties are another hallmark of autism, and they can significantly affect a child’s experience in school. Kids with autism often struggle to interpret social cues, such as body language, facial expressions, or tone of voice.
This can lead to misunderstandings with peers and teachers, making social interactions stressful and confusing.
Because of these social challenges, children with autism might:
- Avoid group activities or playtime with classmates.
- Misinterpret others’ intentions, leading to potential conflicts.
- Have difficulty forming friendships, which can affect their emotional well-being.
This lack of social interaction can lead to feelings of isolation. However, when social skills are taught through structured programs and supported by therapy, children can develop more appropriate social behaviors, making school a more enjoyable experience.
3. Sensory Sensitivities Can Disrupt Learning
Many children with autism experience heightened sensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as bright lights, loud noises, or certain textures. These sensory sensitivities can be overwhelming in the school environment, causing distractions or emotional distress that affects focus and behavior.
For instance:
- Fluorescent lights in classrooms might cause discomfort or anxiety.
- The noise level in a busy cafeteria could be overwhelming, leading to meltdowns.
- Certain clothing or materials may feel irritating, making it hard to concentrate on work.
Special accommodations, like noise-canceling headphones, dimmed lighting, or flexible seating arrangements, can help alleviate sensory stress and improve learning outcomes for students with autism.
4. Behavioral Challenges May Impact Classroom Participation
Behavioral challenges, such as meltdowns, outbursts, or self-stimulatory behaviors (like hand-flapping), are common in children with autism. These behaviors are often a response to sensory overload, stress, or frustration, and they can disrupt classroom activities or hinder the child’s ability to learn.
To address behavioral challenges, educators can:
- Implement positive reinforcement strategies to encourage desirable behaviors.
- Use calming techniques, like deep breathing or sensory breaks, to help children manage anxiety.
- Develop individualized behavior intervention plans (BIPs) tailored to the child’s specific needs.
By understanding the root causes of these behaviors, teachers can respond more appropriately and create a learning environment that minimizes disruptions and maximizes learning opportunities.
5. Difficulty with Executive Functioning Can Impact Organization
Executive functioning refers to a group of cognitive processes that help with planning, organization, problem-solving, and time management. Many children with autism struggle with executive functioning, which can make it difficult to manage assignments, stay organized, or meet deadlines in a classroom setting.
Students with executive functioning challenges may:
- Forget to complete assignments or forget important details.
- Have trouble organizing their school supplies or managing their time effectively.
- Become easily overwhelmed by multi-step tasks or long-term projects.
Support in the form of visual schedules, checklists, and clear instructions can help children with autism manage their tasks more efficiently and reduce frustration.
6. Tailored Teaching Strategies are Essential
Because the effects of autism on education vary from one child to another, it is crucial for teachers to adopt tailored teaching strategies that meet the specific needs of each student. This personalized approach can help children with autism achieve their academic potential and succeed in school.
Some effective strategies include:
- Using visual aids, like charts or graphic organizers, to support learning.
- Breaking tasks into smaller, manageable steps to reduce overwhelm.
- Providing consistent routines and clear expectations can minimize anxiety.
When children with autism receive instruction that is adapted to their unique needs, they are better able to engage with the material and demonstrate their understanding.
7. The Role of Peer Support in Education
While children with autism may face challenges in forming friendships, peer support can play a significant role in enhancing their educational experience. Inclusion programs, where neurotypical children are paired with students on the spectrum, can help foster socialization and promote understanding between students with different abilities.
Benefits of peer support include:
- Improved social interactions and relationship-building skills.
- A sense of community and belonging in the classroom.
- Greater empathy and acceptance among classmates.
By facilitating positive peer interactions, schools can create more inclusive and supportive learning environments for children with autism.
8. Educational Challenges Vary by Age and Stage of Development
The challenges that children with autism face in education can vary significantly depending on their age and developmental stage. Younger children might need more intensive support with basic communication and behavior management, while older students may struggle more with executive functioning and social relationships.
At each developmental stage, children with autism may require different types of support:
- Preschool-aged children may benefit from early intervention programs that focus on socialization and communication.
- Elementary-aged students may need help with academic skills and classroom routines.
- High school students might focus on vocational training, career readiness, and independent living skills.
Tailoring support to the child’s developmental needs ensures they receive the appropriate resources at each stage of their educational journey.
9. The Impact of Autism on Academic Performance
While many children with autism are capable of learning at or above grade level, they may face challenges that affect their academic performance. For instance, difficulties with communication, attention, and social interaction can create barriers to completing assignments or participating in group activities.
However, when children with autism are provided with the necessary support, they can succeed academically. This support might include:
- Individualized instruction in areas of difficulty.
- Use of assistive technology to support communication or learning.
- Regular check-ins to ensure that they are staying on track with assignments.
Proper accommodations can help children with autism meet their academic goals and reach their full potential.
10. How ABA Therapy Supports Educational Success
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) therapy is one of the most effective methods for supporting children with autism in educational settings. ABA focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors and teaching new skills through structured and systematic interventions.
ABA therapy helps autistic children in the education setting by:
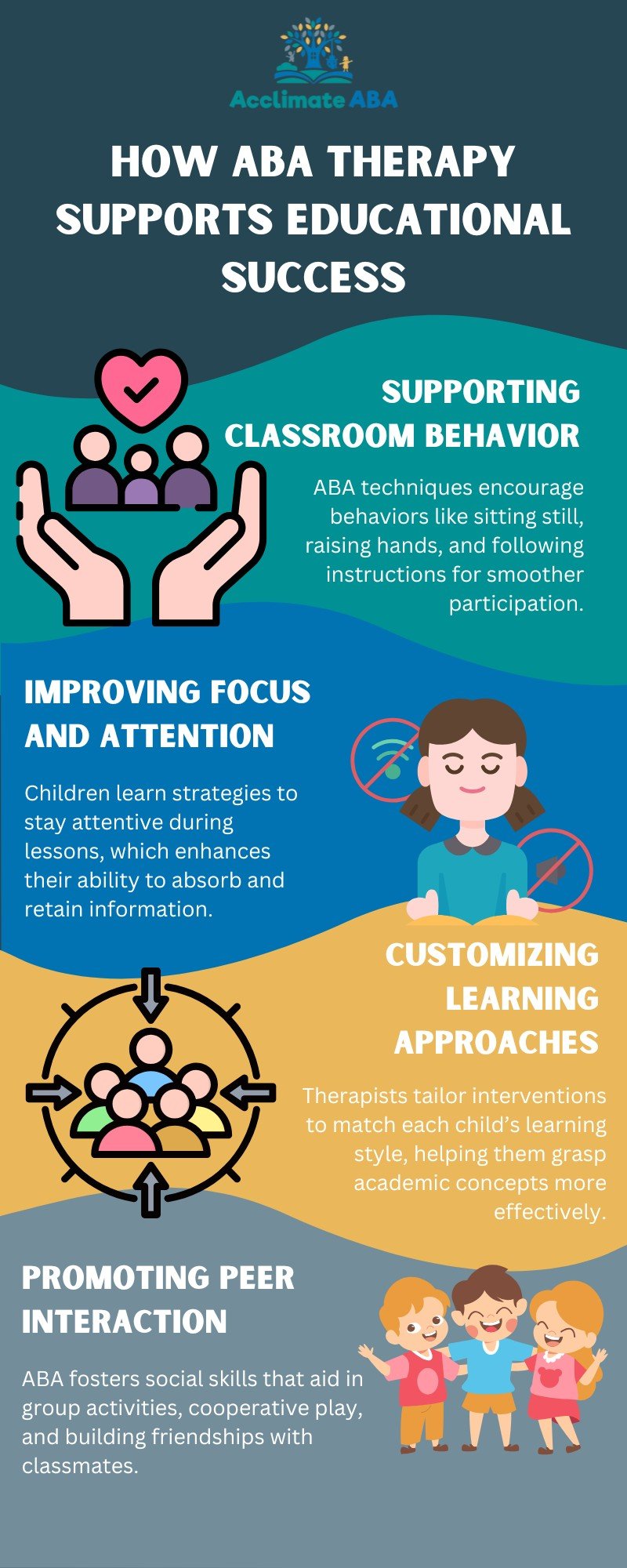
By incorporating ABA therapy into educational plans, children with autism can overcome many of the challenges they face in school and improve their overall learning experience.
Looking to improve health and well-being? Check out our article, “Discover the Best Exercises for Autistic Adults for Better Health.” It offers helpful tips and practical exercises tailored for autistic adults, promoting physical and mental wellness. Don’t miss it for a holistic approach to health!
Discover the Power of ABA Therapy in Utah
If you’re looking for effective solutions to support your child’s education, Acclimate ABA offers top-notch ABA therapy services in Utah. ABA therapy can address the specific challenges your child with autism may face in the classroom, helping them communicate better, engage socially, and perform academically. Don’t wait to give your child the tools they need for success. Contact us today to learn how we can help.
